The Software Licensing Management tool (slmgr.vbs)
is a script you can use to perform several activation tasks. This tool
has many capabilities, including simple tasks, such as rearming or
activating Windows, to more advanced tasks, such as reviewing the
license information or configuring KMS options. The following sections
cover the common uses of slmgr.
Note
Although the following sections show the common uses of the slmgr tool, they are not all inclusive.
Managing Basic Tasks with slmgr
The following table shows the syntax of some basic tasks you can perform with slmgr.
| slmgr Basic Tasks | Comments |
|---|
| Rearm licensing.
C:\>slmgr –rearm | Resets the activation timer or the activation grace period.
Tip
Windows Server 2008 can be installed for an evaluation period of up to
60 days without activation. At the end of the activation period, you can
rearm it for another 60-day period. You can rearm Windows Server 2008
three times for a possible total of 240 days.
|
Install product key.
-ipk product-key
C:\> slmgr -ipk
12345-12345-12345-
12345-12345-12345
| Installs
the specified product key. If a key is already installed, the command
replaces it. This is needed when you are converting a system to use a
different type of activation, such as changing from a retail key to a
KMS key.
Note
The key shown is not a valid key.
|
| Activate Windows.
C:\>slmgr –ato | Activates Windows using the installed product key. |
| Clear the product key.
C:\>slmgr –cpky | Removes the product key from the registry to prevent disclosure attacks. |
| Uninstall the product key.
C:\>slmgr –upk | Uninstalls the product key. |
Viewing License Information with slmgr
There might be times when you just want to view licensing information. You can do so with slmgr, as shown in the following table.
| slmgr License Information Switches | Comments |
|---|
| Display basic license information.
C:\>slmgr –dli | Displays basic license information similar to Figure 1. |
| Display detailed license information.
C:\>slmgr –dlv | Displays more detailed information similar to Figure 2. |
| Show expiration date.
C:\>slmgr –xpr | Shows
the expiration date of the current license period. If the system is in
the grace period, it shows the end of the grace period. If the system is
activated by a Key Management Service (KMS) server, it shows the
expiration date of the KMS license. Retail licenses and Multiple Access
Key (MAK) licenses are permanent and don’t have an expiration after they
are activated. |
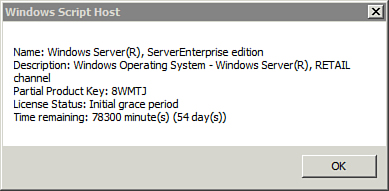
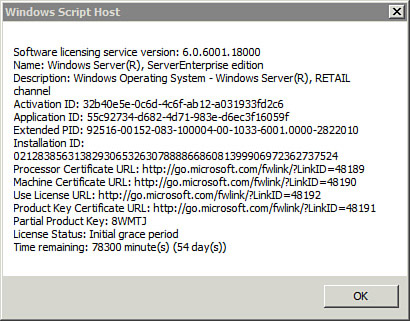
Tip
If the server is activated, these screens provide different activation information depending on the type of activation.
Managing KMS Servers with slmgr
If your organization uses a KMS server, you might need to use slmgr to manage some of the KMS settings as shown in the following table.
| slmgr Switches for KMS Servers | Comments |
|---|
Set the KMS TCP port.
slmgr -sport port-number
C:\> slmgr -sport 1690
| The
default port for KMS is 1688, but you can change it with this command.
Change it if there is a conflict where another service needs this port.
The example changes the port to 1690.
Tip
If you change the port used on the KMS server, you must also change the port used on the KMS clients.
|
Change the activation interval for KMS clients.
slmgr /sai interval-
in-minutes
C:\> slmgr -sai 180
| The
default activation period for KMS clients is 120 minutes, but you can
change it to a number between 15 and 43,200 minutes (30 days). |
Set the renewal interval.
slmgr /sri renewal-
interval-in-minutes
C:\> slmgr -sri 10080
| The
default renewal period for clients is 10,080 minutes (7 days), but you
can change to a time between 15 minutes to 43,200 minutes (30 days). |
| Enable DNS publishing by KMS.
C:\>slmgr -sdns | Ensures that that the KMS server publishes SRV records to the DNS server. This is the default.
Tip
If this is enabled and the SRV records are not created on DNS, you might
need to restart the service that publishes the records. On Windows
Server 2008 the service is slsvc and on Windows Server 2008 R2, it’s
sppsvc.
|
| Disable DNS publishing by KMS.
C:\>slmgr –cdns | Disables publication of the SRV records to the DNS server. |
Using KMS Activation Keys
If you are converting a system to use KMS activation, you can use the slmgr tool. The basic syntax to convert to KMS activation is
slmgr -ipk kms-product-key
The following table shows the KMS product key for some common Windows products.
Tip
These keys are the generic product keys and they let
clients know that they must activate through a KMS server. The KMS
server must have a different key purchased from Microsoft or an
authorized reseller.
| Operating System | KMS Product Key |
|---|
| Windows 7 Professional | FJ82H-XT6CR-J8D7P-XQJJ2-GPDD4 |
| Windows 7 Enterprise | 33PXH-7Y6KF-2VJC9-XBBR8-HVTHH |
| Windows Web Server 2008 R2 | 6TPJF-RBVHG-WBW2R-86QPH-6RTM4 |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard | YC6KT-GKW9T-YTKYR-T4X34-R7VHC |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise | 74YFP-3QFB3-KQT8W-PMXWJ-7M648 |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 Datacenter | 74YFP-3QFB3-KQT8W-PMXWJ-7M648 |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 HPC Edition | FKJQ8-TMCVP-FRMR7-4WR42-3JCD7 |
After installing the key, you can activate the client with the following command:
Managing KMS Clients with slmgr
If you modify some of the settings on the KMS server,
you might also need to modify settings on the KMS clients. The
following table shows some common commands.
| slmgr Switches for KMS Clients | Comments |
|---|
Set the name of the KMS server.
slmgr -skms KMS-server-name
C:\> slmgr -skms kms1
| Sets the name of the KMS server for the client. |
Set the name and port of the KMS server.
slmgr -skms KMS-server-
name:port-number
C:\> slmgr -skms kms1:1688
| The
default port is 1688, so it isn’t needed if the port hasn’t changed on
the KMS server. However, if the port was changed on the KMS server, you
can change it on the KMS client with this command. |
| Clear the KMS information.
C:\>slmgr -ckms | Clears the KMS server name and port number on the client. |
Enable or disable KMS host caching.
C:\> slmgr -skhc
C:\> slmgr –ckhc
| Enables KMS host caching with -skhc and disables it with -ckhc. |